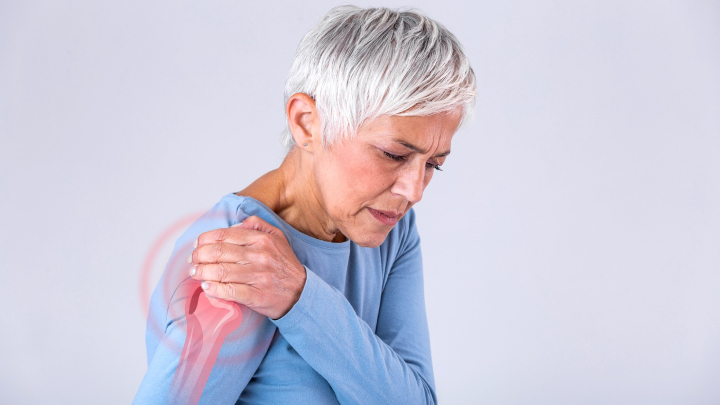
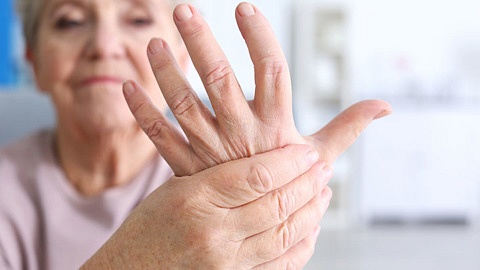
Gout classified as a joint condition categorized alongside osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and others. However it is uniquely different with respect to...
Joint Inflammation and Osteoarthritis
Inflammation is the body’s response to an unwanted stimuli. This response is mediated primarily by the immune system. The main objective of an inflammatory response is to encourage healing. Inflammation can be caused by infections, chemical/ radiation exposure and most commonly, physical injuries. Inflammation that occurs in the body’s skeletal structure such as the joints is often a result of an injury due to overuse or trauma to the area.
The five symptoms of inflammation include:
- Redness
- Heat
- Swelling
- Loss of function
- Pain
Not all five symptoms are always present together. For example an ankle sprain may cause pain, swelling and loss of function but redness and heat may not always occur.
Inflammation is driven by activation of special immune cells, signaling molecules and dilation of blood vessels. These changes allow blood to flow, flooding the injured area with immune cells to directly help heal the tissue and provide further protection. This inflammatory process, when temporary, is beneficial since it encourages healing. However, if the injured tissue has not healed during this acute stage, the inflammatory process no longer encourages healing. Chronic inflammation can cause further damage and result in constant pain, impacting mood, energy and sleep. An individual living with chronic inflammation often experiences a significant decrease in overall quality of life.
Addressing inflammation so that it is beneficial and occurs only for a short time is preferred. However, if chronic inflammation occurs the main goal of treatment is to halt the inflammatory process rather than encourage it.
One of the most common inflammatory conditions is osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis affects both men and women. It occurs in men before 45 years of age and women as they age. Osteoarthritis which occurs in aging adults and is due to the natural loss of cartilage tissue within a joint. As a joint is repeatedly used, the cartilage and components within the joint degrade over time, eventually leading to bone rubbing directly against bone. This activates inflammatory reactions causing pain, stiffness, swelling and difficulty with joint movement. As you continue to age multiple joints in the body can be affected.
The most common joints affected by osteoarthritis include:
• Knees
• Hips
• Shoulders
• Fingers
Addressing inflammation and maintaining healthy joints is critical to preventing further joint cartilage breakdown and reducing symptoms.
Anti-inflammatory medications such as NSAIDs and corticosteroids can help with both chronic and acute inflammation but they do come with unwanted side effects. For example, NSAIDs are linked to gastrointestinal bleeding and corticosteroids can lead to weight gain, blood pressure changes and even mood changes. Surgery is also an option but often reserved for severe osteoarthritis.
There are a number of natural ingredients that can help target the inflammatory cascade and help relieve symptoms associated with joint pain.
Natural anti-inflammatory ingredients:
- Curcumin – derived from the Indian spice turmeric. Curcuminoids have been studied to help reduce inflammatory signalling pathways in the body.
- Boswellia is a resin derived from the boswellia tree. It has historically been used in religious and cultural ceremonies. The resin contains boswellic acids which has shown to reduce inflammatory signalling and help preserve cartilage tissue.
- Omega 3 fatty acids are widely known to help reduce inflammation, including joint-related inflammation
- Glucosamine is a component of cartilage tissue and degrades overtime. Studies involving knee osteoarthritis have reported supplementation with glucosamine can help reduce pain and preserve cartilage tissue after a minimum of four weeks use.
Natural agents such as those listed above can help ease ongoing inflammation associated with osteoarthritis. Addressing inflammation directly not only helps reduce pain, swelling and joint function but also benefits an individual’s overall quality of life.
Related Posts
Your immune system is a complex network of different cells with a range of signals that help guide the proper upkeep of your entire body. Most are familiar...
Caring for your joints is vital to living a healthy and happy life. Use these natural tips to better care for your joints and live more comfortably.
Click...
Your immune system is a complex network of different cells with a range of signals that help guide the proper upkeep of your entire body. Most are familiar...
Caring for your joints is vital to living a healthy and happy life. Use these natural tips to better care for your joints and live more comfortably. Click...
Categories
- Allergy Relief
- Bell Lifestyle News
- Brain and Vision Health
- Depression
- Digestive Health
- Eating Healthy
- Energy Boosts
- Fitness
- Foods for Energy
- Heart and Lung Health
- Herbs
- Immune System Support
- Lifestyle
- Men's Health
- Mental
- Motivation
- Natural Remedies
- Nutrition
- Pain Relief
- Physical
- Recipes
- Relationships
- Sexual Health
- Skin and Hair Health
- Sleep Health
- Social
- Stress Relief
- Uncategorised
- Videos
- Weight Management
- Women's Health
- Your Wellness Now
Follow us on Twitter
#90 Bladder One for Women™ is a convenient one-a-day capsule for urinary tract health, featuring herbal extracts in… twitter.com/i/web/status/1…
May 2023Urinary tract infections - UTI: To treat or prevent? That is the question. Find out more about causes and treatme… twitter.com/i/web/status/1…
May 2023"How you feel is very important to how you look. Healthy equals beautiful." - Victoria Principal #womenshealth https://t.co/OPShoEbOXb
May 2023
© Copyright 2024. All rights reserved.